




















EUR
en
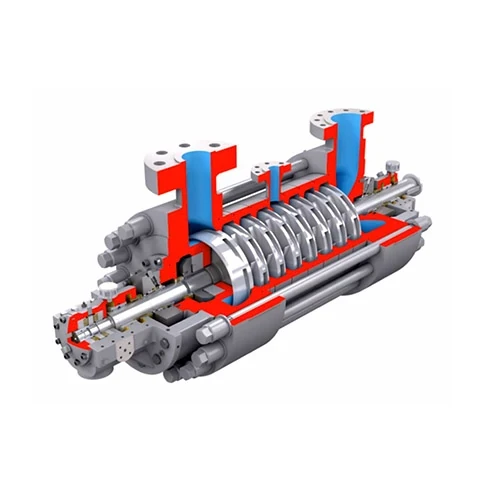
Mud pump fluid end parts serve as the hydraulic powerhouse of drilling operations, playing a pivotal role in maintaining wellbore stability and operational efficiency. These components operate under extreme pressures (up to 7,500 psi) while handling abrasive fluids containing 20-30% solid particles.
1. **Pressure Generation**: Converts mechanical energy into hydraulic power to circulate drilling mud 2. **Debris Management**: Removes cuttings while cooling the drill bit 3. **Pressure Maintenance**: Creates hydrostatic pressure to prevent formation fluid influx
Key operational challenges include:
The fluid end’s performance relies on precise coordination between:
This guide systematically examines 10 essential components, their failure modes, and maintenance strategies to optimize pump lifespan and drilling efficiency. Subsequent sections will detail specific parts like ceramic liners that demonstrate 280% longer service life compared to standard bimetal versions in shale gas applications.
The structural backbone of the system, fluid end housings are forged from 4130/4135 alloy steel per API 7K standards, undergoing triple heat treatment to achieve:
This reciprocating duo handles the most abrasive wear, with material pairings determining operational lifespan:
| Component | Material Options | Key Properties | Wear Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liners | Bimetal (Cr26-28% inner), Ceramic (ZrO₂) | HRC 58-62 hardness, 0.25mm max ovality | Middle-section scoring, tell-tale leakage ports |
| Pistons | Polyurethane (HNBR), Nitrile Rubber | 70MPa tensile strength, 1000% elongation | Groove depth >3mm, extrusion deformation |
Ceramic liners demonstrate 280% longer service life in shale gas applications due to zirconia’s ultra-low wear rate (0.08mm/1000hrs) compared to standard bimetal versions. Piston velocity peaks at mid-stroke (4-6 m/s), creating a characteristic “hourglass” wear pattern.
The hydraulic check valves employ three dominant designs:
Critical maintenance involves:
The fluid routing network combines:
**Suction Manifold**
**Discharge Manifold**
Sealing systems utilize:
Optimal performance requires synchronized operation:
Field data shows ceramic liners paired with HNBR pistons reduce fluid end maintenance intervals by 75% in abrasive formations. This systemic approach underscores why comprehensive fluid end management outperforms individual component optimization.
Mud pump fluid end parts operate under extreme conditions, facing challenges from abrasive wear, cyclic loading, and chemical corrosion. These components are critical for maintaining drilling efficiency, yet they are prone to specific failure modes that can significantly impact operational performance. Understanding these failures and implementing proactive maintenance strategies is essential for minimizing downtime and extending component lifespan.
The liner-piston system is particularly susceptible to abrasive wear, with distinct patterns indicating different failure mechanisms:
**Common Wear Patterns and Prevention:**
| Wear Type | Causes | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Hourglass wear | Mid-stroke piston velocity (4-6 m/s) causing uneven abrasion | Rotate pistons 90° weekly; use ceramic liners with ZrO₂ coating |
| Ovality deformation | Side load exceeding 500 MPa endurance limit | Maintain API 7K-compliant alignment (<0.25mm tolerance) |
| Groove formation | Solid particle embedment (20-30% content) | Install magnetic filters; maintain mud viscosity 35-45 sec/qt |
| Thermal cracking | >80℃ temperature fluctuations | Monitor cooling system; use HNBR pistons (1000% elongation) |
Ceramic liners demonstrate 280% longer service life compared to standard bimetal versions in shale gas applications due to zirconia’s ultra-low wear rate (0.08mm/1000hrs). Regular inspection should focus on middle-section scoring and leakage port discoloration as early wear indicators.
Valve assemblies account for 42% of fluid end failures, primarily due to:
Field data indicates paired replacement of valves/seats improves mean time between failures (MTBF) by 58% compared to individual component changes. Copper anti-galling paste should be applied to thread connections during installation.
Seal failures lead to 30% volumetric efficiency loss, with critical considerations:
**Material Selection Guide:**
Weekly maintenance should include:
Implementing IoT-enabled wear detection systems can predict seal failure 72 hours in advance, reducing unplanned downtime by 85%.
| Component | Failure Sign | Action Interval | Critical Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pistons | >3mm groove depth | 250 operating hours | Dial indicator |
| Valve seats | 0.5mm pitting | 500 hours/paired replacement | Bore scope |
| Manifold seals | Visible extrusion | Weekly torque check | Laser alignment tool |
| Housing | >0.5mm crack | API 7K phased array UT | Ultrasonic tester |
Proactive maintenance following these guidelines can extend fluid end service life by 40% in abrasive formations while maintaining 92% volumetric efficiency throughout the drilling cycle.
Proper installation of mud pump fluid end parts is critical to ensure operational reliability and longevity. According to industry data, 60% of premature failures stem from improper installation practices such as misalignment or inadequate torque application. This section outlines systematic procedures to achieve optimal performance while complying with API 7K standards.
Before assembly, verify component readiness through these steps:
Post-installation pressure testing follows a phased approach:
| Phase | Procedure | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrotest at 1.5x working pressure (11,250 psi for 7,500 psi systems) | No visible leakage for 30 mins |
| 2 | Cyclic loading (500 cycles between 20%-100% rated pressure) | Pressure drop <2% per cycle |
| 3 | Thermal shock test (-20°C to 80°C fluid temperature swings) | No flange bolt loosening |
Critical notes:
Adhere to these mandatory practices during commissioning:
| Component | Torque Value (ft-lb) | Lubrication Required |
|---|---|---|
| Valve Cover Bolts | 450-500 | Molykote 111 |
| Manifold Flanges | 1,200-1,300 | Never-Seez |
Final commissioning requires signed checklists documenting:
The mud pump fluid end industry is undergoing a transformative phase with material advancements that significantly enhance component longevity and operational efficiency. These innovations address critical challenges such as abrasive wear, corrosion, and fatigue failure in extreme drilling environments.
Modern fluid end components increasingly utilize advanced ceramics and composites to combat wear and corrosion:
**Ceramic Liners (ZrO₂)**
**Composite Coatings**
| Material Type | Key Properties | Application Range |
|---|---|---|
| 20CrMnTi alloy | HRC 60+, σb≥850MPa | Conventional wells <5,000 psi |
| Nitrogen-doped SiC | 15% higher fracture toughness | HPHT wells >15,000 psi |
| HNBR-PTFE blends | 1000% elongation, pH 1-13 resistance | Acidic drilling fluids |
IoT-enabled systems are revolutionizing predictive maintenance through real-time performance tracking:
**Wear Detection Systems**
**Digital Twins**
**Edge Computing**
Emerging material technologies show promising laboratory results:
These innovations align with API 7K-2026 draft standards emphasizing:
The mud pump fluid end market is dominated by several key manufacturers, each bringing unique innovations and reliability to the table. This section compares leading brands based on their technological advancements and field-proven performance.
**NOV’s Mission Blak-JAK™ PowerLast Fluid End**sets a new standard for high-pressure drilling with its 10,000 psi-rated design, reducing downtime through simplified maintenance. Key features include:
Premium Oilfield’s**Sur-Lock® Quick Change Systems**revolutionize maintenance efficiency:
_Comparative Advantage Table:_
| Feature | NOV Blak-JAK™ | Premium Sur-Lock® |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | 10,000 psi | 7,500 psi |
| Valve Change Time | 15 minutes (standard) | <1 minute |
| Liner Material Options | Ceramic/Bimetal | Zirconia/Chrome Iron |
| API 7K Compliance | Full | Full with enhanced seal |
Gardner Denver’s**VX Fluid End**redefines cost-performance ratios with:
Sunnda Corporation specializes in**Fast-Change Expendables**:
_Material Science Breakthroughs:_
For optimal component selection, consider these manufacturer-specific advantages:
| Operational Requirement | Recommended Solution | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-HP Shale Drilling | NOV Blak-JAK™ + Ceramic Liners | 10,000 psi rating with 85% MTBF improvement |
| Fast-Paced Workover Rigs | Premium Sur-Lock® + Caliber N4 | Valve changes <2 minutes |
| Abrasive Formation | Sunnda Zirconia Liners | 0.08mm/1000hrs wear rate |
| Budget-Constrained Ops | GD VX Fluid End | 40% lower TCO with Redline+ parts |
Field data shows NOV’s ceramic liners paired with Premium’s Sur-Lock® systems reduce fluid end maintenance costs by 58% in extended-reach drilling. For corrosive environments, Sunnda’s 4Web valves with HNBR seats outperform standard designs by 3x lifespan in H₂S-rich wells.
Mud pump fluid end parts represent the critical hydraulic interface in drilling operations, where component selection and maintenance directly impact operational safety and efficiency. As demonstrated throughout this guide, these components endure extreme conditions including 7,500 psi cyclic loading, 20-30% abrasive solids content, and corrosive drilling fluids.
**Material Selection Matrix**
Adopt advanced materials to combat prevalent failure modes:
| Failure Mode | Solution | Performance Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive wear | ZrO₂ ceramic liners | 280% lifespan increase in shale gas |
| Fatigue fracture | 20CrMnTi alloy valves (HRC 60+) | 40% longer life at 15,000 psi |
| Chemical corrosion | HNBR-PTFE seals | pH 1-13 resistance |
| Thermal stress | Graphene-enhanced manifolds | 40% higher thermal conductivity |
**Critical Standards**
**Technical References**
Proactive adherence to these guidelines can reduce fluid end maintenance costs by 58% while extending mean time between failures by 40% in abrasive formations.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.