




















EUR
en
When you invest in a water well drilling rig, a mud pump is important-it's a non-negotiable partner. You can picture the drilling rig as the muscle that breaks through rock, and the mud pump as the guardian that ensures safety, stability, and efficient progress. The rig's primary function is to rotate the drill bit at high speed to cut through various strata-whether clay, sand, or hard rock. But without the mud pump's support, drilling progress quickly comes to a standstill.
The mud pump's primary function is to circulate drilling fluid ("mud") at high pressure, providing several essential safeguards. It continuously cools the drill bit-which can generate frictional heat of up to 300°C-and lubricates the contact surfaces, extending bit life by 30–50%. At the same time, it transports cuttings (rock chips and sand) back to the surface, preventing debris buildup that leads to re-cutting or even drill jamming. Just as importantly, the pump maintains downhole pressure balance: too little pressure risks blowouts when high-pressure gas or oil surges into the well, while too much can cause mud loss into low-pressure formations. In addition, the colloidal particles in the mud form a thin "mud cake" on the well wall, reinforcing loose layers and preventing collapse. The mud pump is the power heart of the drilling system-and selecting the right one has a direct impact on drilling safety and efficiency.
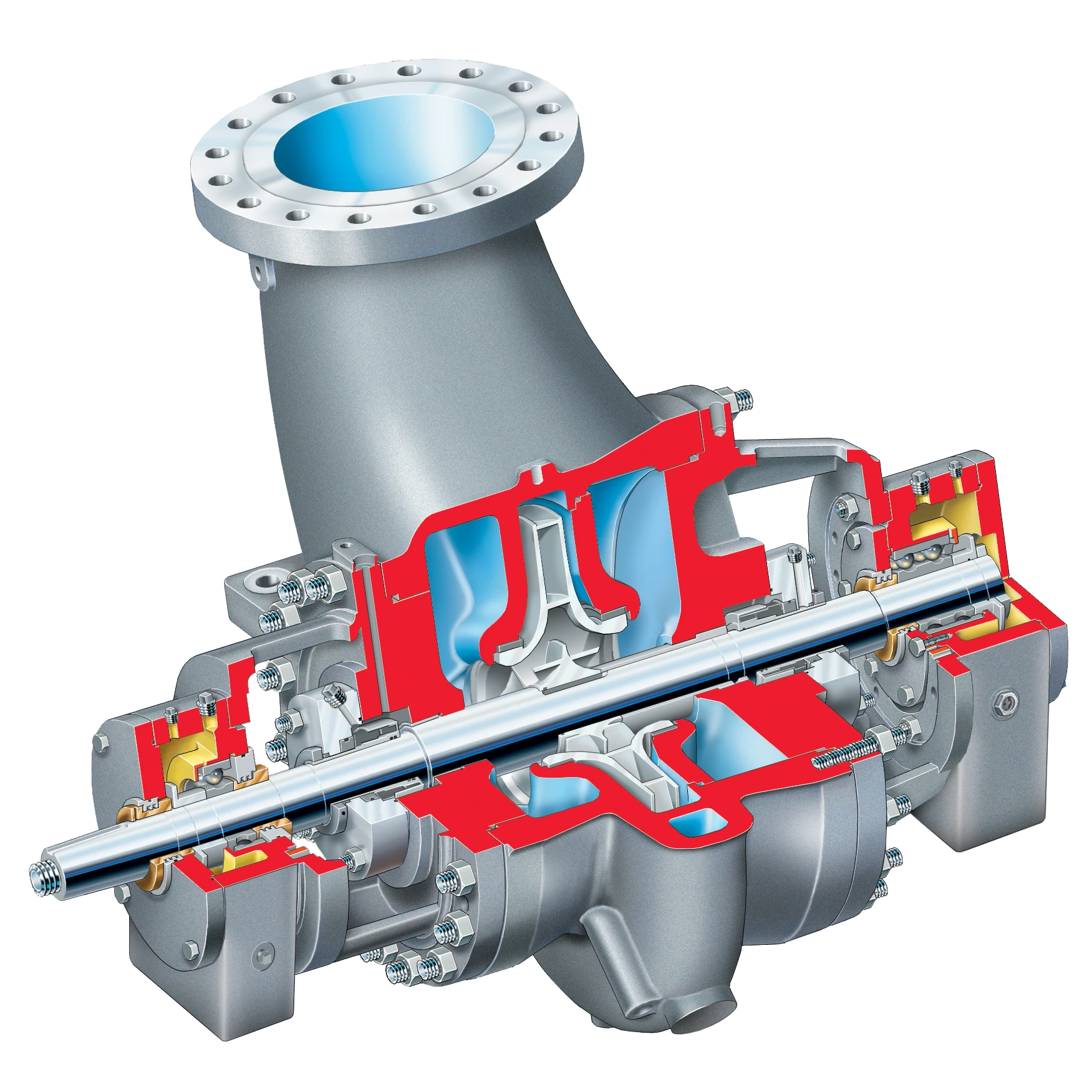
A mud pump is a mechanical device that delivers flushing fluids (water, mud, or polymer solutions) into the drill hole during drilling. It's the backbone of drilling equipment, especially in positive-circulation drilling-the most common method for water wells. Here's how it works: the pump pushes fluid through high-pressure hoses, a swivel, and the drill pipe's central hole to the bit's tip. This fluid cools the bit, flushes cuttings to the surface, and stabilizes the well.
Most mud pumps for water wells are either piston-type or plunger-type, both driven by a power unit: the crankshaft rotates, moving the piston/plunger back and forth in the cylinder, and check valves alternate to suction and discharge fluid.
► Pro Tip: Choose a pump with slightly higher flow and pressure than required. This margin not only ensures steady performance but also increases drilling speed-for example, pairing a BW450 with an RCF200C can drill through sandstone up to 20% faster than with an undersized pump.
The synergy between the rig and the mud pump forms a closed-loop system, where every stage of drilling relies on the pump's performance:
► Fluid Delivery: The mud pump pushes water (or drilling mud) down the drill pipe. The fluid travels to depths of hundreds of feet and exits through small ports in the drill bit.
► Cutting Removal: As the bit cuts through rock, the fluid fills the borehole and lifts loose cuttings-sand, gravel, or rock chips-upward through the annular space between the pipe and well wall, carrying them to the surface.
► Speed Matching: A capable pump clears cuttings at the same rate the rig drills. For example, our BW250 mud pump maintains stable pressure to match the RCF180S rig's penetration speed, preventing delays from cuttings buildup.
When the mud pump underperforms-or if the pump is mismatched with the rig-efficiency drops sharply. If flow rate is too low, cuttings settle at the bottom, forcing the bit to grind the same material again. We've seen projects where undersized pumps turned a 10-day well drill into a 3-week slog-wasting time and labor costs.
Choosing a mud pump isn't just about picking a model-it's about matching it to the unique requirements of your project. Here are the four critical factors to consider:
Drilling depth is the first deciding factor:
Always verify compatibility with your rig's power rating. For example, a 50 kW rig such as the RCF180S cannot drive a BW600 (designed for rigs above 100 kW). Oversizing not only wastes fuel but can also overload and damage the engine.
The geological conditions of the well also influence pump selection:
Even a high-quality pump requires regular care to maintain performance and extend service life. Follow these practices:
★ Daily checks: Inspect oil levels in the gearbox and hydraulic system, check hoses and seals for leaks, and clean the suction filter. (Debris here can cause piston wear.)
★ Weekly servicing: Replace lubricating oil with the grade specified in the Ran Cheng manual. Inspect pistons and plungers-if a piston's diameter has worn by 1 mm or more, replace it with a Rancheng original part for a proper fit.
★ Long-term storage: After the project, flush the pump with clean water to remove residual mud, which can harden and corrode components. Apply anti-rust oil to exposed metal surfaces before storage.
Choosing the right mud pump is just as critical as selecting the rig itself. It directly impacts drilling speed, safety, and cost-efficiency. If you're uncertain which model best suits your needs, the Rancheng technical team can evaluate your depth, formation, and rig specifications to recommend the optimal solution. With the right mud pump, your water well drilling projects will be faster, safer, and more profitable.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.