




















EUR
en
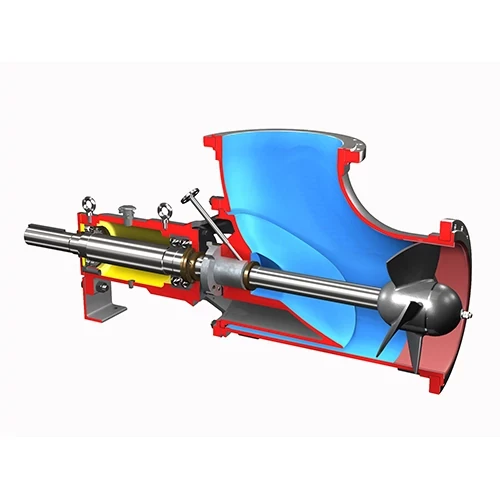
Self-priming pumps are designed to eliminate the need for manual priming, which involves filling the pump and suction lines with liquid before starting the pump. This feature makes self-priming pumps particularly useful when dealing with suction lifts, where the pump is situated above the liquid source. The working principle behind self-priming pumps involves a specialized impeller design and air-water separation mechanisms. The impeller is designed to handle air-water mixtures, allowing the pump to automatically expel air and establish a continuous flow of liquid.
These pumps find applications in various industries, such as construction, agriculture, and wastewater management. They are advantageous in scenarios where frequent priming is impractical or time-consuming, making them ideal for intermittent operations and locations with unreliable water sources.
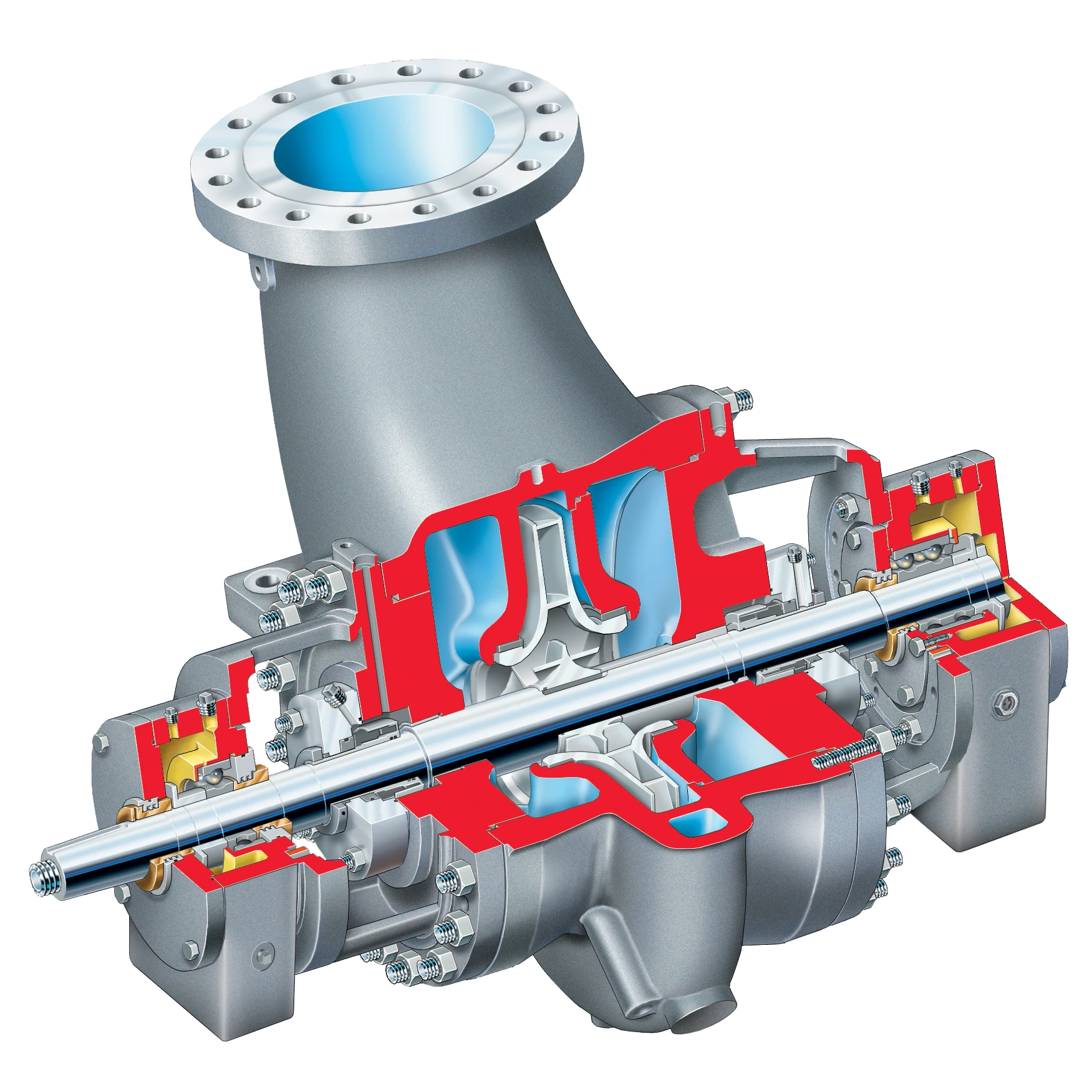
Centrifugal pumps are the most common type of pumps used in industrial settings. They work based on the principle of centrifugal force, where a rotating impeller accelerates the fluid outward, creating a pressure gradient that propels the fluid through the pump. However, traditional centrifugal pumps face priming challenges, especially in cases where the pump is not located below the liquid source. These pumps rely on gravity to help fill the pump and suction lines with liquid, making manual priming or external priming methods necessary.
Choosing the appropriate pump for a specific application involves considering several factors. The nature of the fluid being pumped, including its viscosity and corrosiveness, impacts the pump’s material selection. Flow rate and pressure requirements determine the pump’s size and capacity. The layout of the system and space constraints dictate the pump’s configuration. Initial cost and long-term operational costs influence the overall economic feasibility, while energy efficiency and environmental considerations play a role in sustainable pump choices.
In a real-world context, self-priming pumps are commonly found in agricultural settings where water needs to be lifted from wells or underground sources. For instance, in remote areas with inconsistent water availability, self-priming pumps provide reliable water supply without the need for constant manual intervention. On the other hand, centrifugal pumps are often used in large-scale industrial processes. An example is the circulation of cooling water in power plants, where centrifugal pumps efficiently transport large volumes of water for heat dissipation.
The future of pump technology involves continuous improvements in efficiency, automation, and sustainability. Self-priming pumps are likely to see advancements in air-handling mechanisms, allowing them to handle even more challenging conditions. Centrifugal pumps could incorporate enhanced impeller designs and control systems to increase efficiency and adapt to changing operational demands. Automation and smart technologies are poised to make pumps more responsive and energy-efficient, contributing to reduced downtime and operational costs.
In summary, the choice between self-priming and centrifugal pumps depends on the specific application requirements. Self-priming pumps excel in scenarios where automatic priming is essential, such as suction lifts and intermittent operations. Centrifugal pumps, despite priming challenges, remain versatile workhorses for various fluid transport applications. Proper consideration of selection factors and understanding the differences between these pump types is crucial for optimizing system efficiency, minimizing costs, and ensuring reliable fluid movement across industries.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.