




















EUR
en
Centrifugal pump has many advantages such as a wide range of performance, uniform flow, simple structure, reliable operation and convenient maintenance, so the centrifugal pump is the most widely used in industrial production. Except for reciprocating pumps for high pressure and small flow or metering, vortex pumps and positive displacement pumps for liquids containing gas, and rotor pumps for high-viscosity media, water pumps are used in most other occasions. According to statistics, in chemical production (including petrochemical) installations, the use of centrifugal water pumps accounts for 70% to 80% of the total pumps. What can a centrifugal pump do? How does a centrifugal pump work?
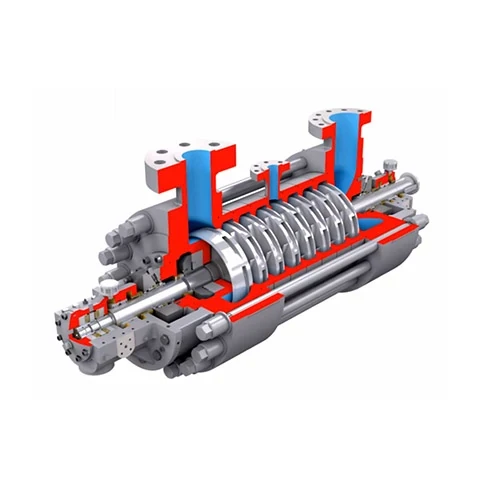
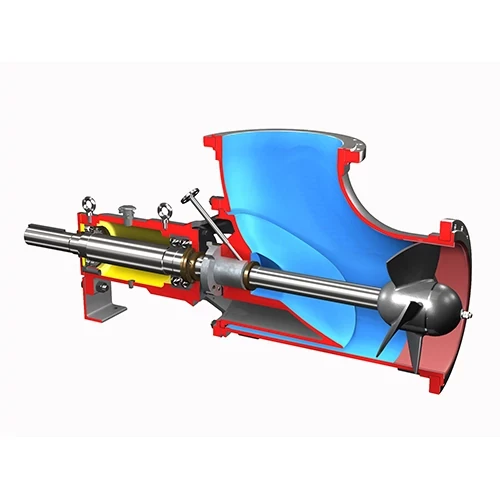
The centrifugal pump is mainly composed of impeller, shaft, pump casing, shaft seal and sealing ring, etc. Generally, the centrifugal pump should be full filled with liquid before starting. When the prime mover drives the pump shaft and the impeller to rotate, the liquid moves in a circular motion with the impeller, and is thrown out from the center of the impeller to the periphery under the action of centrifugal force. The liquid gets pressure energy and velocity energy from the impeller. When the liquid flows through the volute to the discharge port, part of the velocity energy will be converted into static pressure energy. When the liquid is thrown from the impeller, the center of the impeller is a low pressure area, which forms a pressure difference with the pressure of the suction liquid surface, so the liquid is continuously sucked, and discharged with a certain pressure.
A. Pump casing. There are two types of pump casings, axial split type and radial split type. The pump casing of most single-stage pumps is volute type, and the radially split pump casing of multi-stage pumps is generally annular or circular. Generally, the inner cavity of the volute pump casing is a spiral liquid channel, which is used to collect the liquid thrown from the impeller. Then the liquid flows trough the diffusion pipe to the outlet of the centrifugal suction pump. The pump casing withstands the full operating pressure and thermal load of the liquid.
B. The impeller is the only working part, and the centrifugal pump does work on the liquid through the impeller. There are three types of impellers: closed, open and semi-open. The closed impeller consists of blades, front cover and rear cover. The semi-open impeller consists of blades and rear cover. Open impeller only has blades, no front and rear covers. Closed impeller is more efficient, open impeller is less efficient.
C. Seal ring. The sealing ring plays a crucial role in preventing both internal and external leakage in a pump. It is typically made of a wear-resistant material and is installed in the pump casing, as well as the front and rear cover plates of the impeller. The primary function of the sealing ring is to create a tight seal between these components, ensuring that no fluid escapes from the pump’s internal chambers or enters from external sources. Over time, due to wear and tear, the sealing ring may need to be replaced to maintain its effectiveness. By regularly inspecting and replacing worn sealing rings, the pump’s performance can be preserved, minimizing leakage and maintaining efficient operation.
D. Shafts and bearings. In a centrifugal pump, the impeller is typically fixed at one end of the pump shaft, while the coupling is installed at the other end. The impeller is responsible for imparting kinetic energy to the fluid, while the coupling connects the pump shaft to the motor or engine that drives it. The type of bearing used in the pump depends on its size. Smaller centrifugal pumps often utilize rolling bearings, which consist of balls or rollers that facilitate smooth rotation. Larger pumps, on the other hand, may employ sliding bearings, which involve a sliding surface that allows the shaft to rotate with minimal friction. The selection of the appropriate bearing ensures proper support and longevity for the pump’s shaft and impeller assembly.
E. Shaft seal. Shaft seals are essential components in pumps for preventing fluid leakage along the shaft. Two common types of shaft seals are mechanical seals and packing seals. Mechanical seals use rotating and stationary parts with a sealing interface to create a tight seal. They offer higher efficiency and reduced leakage compared to packing seals, making them suitable for various pump applications. Packing seals, on the other hand, involve packing material tightly wrapped around the shaft to create a seal. Centrifugal conveying pumps are often designed to accommodate both packing seals and mechanical seals, providing flexibility for different operational requirements and preferences. This allows users to choose the appropriate sealing method based on factors such as the pumped fluid, pressure, and temperature conditions.
1. Prepare the necessary tools. 2. Confirm that the equipment installation and the instrumentation equipment work has been completed. 3. Check whether the oil level in the oil window and oil pot is normal (1/2 to 2/3 of the oil window, the oil cup is full). 4. When the coupling is turned by hands, it should feel easy and rotate evenly, and pay attention to identify whether there is friction and foreign matter in the centrifugal suction pump. 5. When the installation position is below the liquid level (perfusion condition), open the suction pipe valve before starting, so the centrifugal conveying pump can be full filled with liquid. If the centrifugal pump is installed above the liquid level (vacuum condition), the pump should be primed or vacuumed before starting, so the pump and suction pipe can be full filled with liquid and has no air. 6. Open the switch valve (if any) on the mechanical sealing water and cooling water pipe to check whether the flow pressure is normal. 7. After the new installation or maintenance of the motor, the coupling should be disconnected, start the motor to check the forward and reverse rotation of the motor, and then reinstall the coupling after confirming that the forward and reverse rotation is normal.
1. Close the outlet valve. 2. Start the motor. 3. Check whether the centrifugal pump has abnormal noise, vibration, and whether the bearing temperature, outlet pressure, current is normal. 4. Open the outlet valve slowly until the desired position. 5. Check the ammeter, the current must not exceed the rated current on the motor nameplate. 6. Check for shaft seal leaks. 7. For the centrifugal pump with automatic start function, please contact the central control to confirm the pump runs normally, then check the standby pump according to the above steps. Open the inlet and outlet valves of the standby pump, and set the pump to automatic on the central control DCS.
1. Close the outlet valve of the centrifugal pump 2. Stop the motor. 3. Close the inlet valve. 4. Close the valve on the seal flushing fluid and cooling water pipeline (maintain a certain flow to prevent freezing when the ambient temperature is low). 5. If the ambient temperature is lower than the freezing point of the liquid, the liquid in the centrifugal suction pump should be drained to prevent freezing and cracking. 6. If the medium is easy to crystallize or contains more solid particles, it should be rinsed to prevent crystallization or scaling, which is conducive to normal start-up in the future. 7. The regular turning should be carried out for long-term shutdown, and the power should be cut off.
A. Confirm that the pump B is ready to start. B. Start pump B according to the steps of turning on the pump and check the operation of pump B. C. Slowly open the outlet valve of pump B, while slowly closing the outlet valve of pump A.The flow and pressure must be kept stable until the outlet valve of pump B is fully opened and the outlet of pump A is fully closed. Confirm again that the flow and pressure are stable, and stop the pump A motor after one to two minutes of observation. D. Close the inlet valve of pump A, and turn off the cooling water according to the bearing temperature. E. Open the inlet and outlet pipes of the centrifugal pump and the drain valve of the pump body, drain the liquid in the pipeline and the pump body, then close each drain valve.
A. Always check whether the outlet pressure, flow, and current of the centrifugal pump are within the rated range, and never allow the operation beyond the index. B. Always check the motor bearing, motor body, pump bearing, and centrifugal pump body for noise. When the noise is serious, stop the centrifugal pump to check and repair. C. Check whether the operating temperature of each part is within the allowable range. The temperature rise of the pump bearing cannot be greater than 35℃. The maximum temperature cannot exceed 75℃(the conveying high temperature medium should be less than or equal to 90℃). D. Pay attention to the oil level in the bearing seat and observe whether there is oil leakage. The lubricating oil level should be between 1/2 and 2/3. Check whether the lubricating oil is qualified, and replace it immediately when it deteriorates and contains water. Generally, replace the new oil once after 1500 hours of operation. E. Check whether the cooling water and sealing water of each part are unblocked to prevent interruption. F. The centrifugal pump should not run for a long time below 30% of the design flow. Install bypass valve if necessary. G. Check sealing device for leaks. H. Fill in the pump’s operating record. I. Keep the centrifugal pump area and pump body cleaning.
A. Insufficient pump flow
Pump outlet pressure is too high: Open the outlet valve wide until reaching the operating point. The gas in the pump and pipeline is not completely discharged, and the water in the pump is insufficient: Centrifugal pumps and pipelines are completely drained or fully filled with water. Inlet pipeline and impeller are clogged: Clear the blockages in pipes and pumps. Insufficient supply of inlet pipeline: Fully open the valve on the inlet pipeline and check the filter on the inlet pipeline. Too much wear in the pump: Replace worn parts. Insufficient cooling water or blocked cooling cavity: Increase the flow of cooling water, clean the cooling cavity, and replace the clean cooling water. Mechanical failure: Replace worn parts.
B. Motor overload
There is friction between the impeller and the pump body: Check the impeller position, check the piping connections to make sure the centrifugal pump is not stressed. Too much axial force: Clean the impeller balance hole.
C. Shaft seal leaking too much
The bushing surface is rough, and there are grooves or scratches on it: Replace with new bushing. Insufficient cooling water or blocked cooling cavity: Increase the flow of cooling water, clean the cooling cavity, and replace the clean cooling water.
D. Unstable operation of centrifugal pump
The gas in the pump and pipeline is not completely discharged, and the water in the pump is insufficient: Centrifugal pumps and pipelines are completely drained or fully filled with water. Too much wear in the pump: Replace worn parts. There is friction between the impeller and the pump body: Check the impeller position, check the piping connections to make sure the centrifugal pump is not stressed. Too much axial force: Clean the impeller balance hole and install a new gasket. Bearing damage: Replace bearings.
E. The temperature inside the centrifugal pump is too high
The gas in the pump and pipeline is not completely discharged, and the water in the pump is insufficient: Centrifugal pumps and pipelines are completely drained or fully filled with water. Too much wear in the pump: Replace worn parts. Circulating water supply system failure: Check the water supply system, check whether the circulating cooling water filter is blocked, and increase the cross-sectional area of the water supply system pipeline.
F. The outlet pressure of centrifugal pump is too high
Rotation speed is too high: Reduce speed. Outlet pipeline or valve is blocked: Replace or clean valve.
A centrifugal pump is a commonly used fluid delivery device that draws fluid from the inlet into the pump through centrifugal force and pushes the fluid toward the outlet through centrifugal force. The following are conclusions about the working principle and operating procedures of centrifugal pumps: Working principle: The working principle of a centrifugal pump is based on the action of centrifugal force. As the pump rotor rotates, fluid is drawn into the center of the pump and pushed outward due to centrifugal force. Centrifugal force imparts kinetic energy to the fluid and pushes it through the outlet of the pump. Operating procedure: The operating procedure of a centrifugal pump usually includes the following steps: a. Preparation: Make sure the pump is installed in the correct location and check the inlet and outlet pipes and valves for smoothness. b. Start the pump: Start the pump gradually according to the manufacturer’s instructions and avoid sudden flow changes. Monitor pump operation, parameters such as temperature, pressure and vibration. c. Flow control: Control the flow by adjusting the speed of the inlet valve or pump according to project requirements. Avoid overload operation and ensure that the pump operates within a safe operating range. d. Shut down the pump: Gradually reduce the flow rate and stop the pump according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Close the inlet valve and cut off the power supply. e. Maintenance and maintenance: Clean the inlet and outlet pipes of the pump regularly, check and replace worn parts, and lubricate bearings. Perform routine maintenance according to manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines. By following the working principles and operating procedures of a centrifugal pump, you can run a centrifugal pump efficiently. Correct operation and regular maintenance will improve the efficiency and reliability of the centrifugal pump and ensure its stable operation for a long time.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.