





















EUR
en
Dredging operations are essential processes that involve removing sediments—such as sand, gravel, and mud—from the water surface of rivers, lakes, ponds, and other waterways. These operations play a critical role in maintaining navigable channels, preventing flooding, and supporting construction projects in aquatic environments. Among the specialized equipment used in these projects are gold dredges, designed to extract gold from placer deposits in riverbeds and lake bottoms. Floating gold dredges, in particular, have revolutionized the way miners extract gold, enabling efficient, targeted removal of gold-bearing sediments without the need for extensive land-based infrastructure.
Over the decades, dredging has evolved from simple manual methods to highly efficient, mechanized processes. Modern dredges are engineered to handle a variety of materials and site conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of projects—from clearing silted waterways to supporting large-scale construction and mining operations. The ability to float enables these machines to access remote or shallow areas, improving project efficiency and reducing environmental impact. As technology advances, dredging operations are becoming increasingly sustainable and environmentally friendly, ensuring that vital waterways remain functional and that valuable resources like gold can be extracted with minimal disruption to aquatic ecosystems.
The effectiveness and success of a floating dredge in any dredging project depend heavily on its innovative design features, which enhance its mobility, stability, and sediment-handling efficiency. As a machine engineered for performance, a floating dredge is built to operate efficiently in diverse aquatic environments, and its design continues to evolve to meet increasingly complex operational demands.
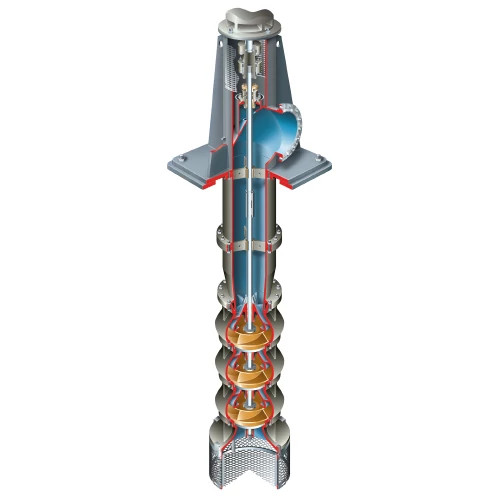
Modern floating dredges typically use pontoon-based platforms made of corrosion-resistant metals or composite materials, offering excellent buoyancy and long-term durability. Steel is commonly used in pontoon construction due to its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of the dredging equipment. These platforms are designed for modular construction, allowing individual components to be transported separately and quickly assembled on-site. This modularity significantly enhances project flexibility, allowing for rapid deployment and minimizing downtime between jobs.
EDDY Pump’s floating dredge models feature a low center of gravity and a wide, stable flotation base, specifically engineered to maintain balance even in turbulent water, fluctuating water levels, or strong currents. This design ensures the dredge remains steady during operations, preventing tipping or instability that could jeopardize safety or efficiency. The platform’s robustness supports heavy dredging equipment, enabling the system to handle challenging dredging tasks in harsh or uneven underwater terrain.
One of the greatest advantages of floating dredges is their ability to operate in sensitive or environmentally delicate areas such as wetlands, shallow shorelines, or ecologically protected water bodies. Because these dredges float on the surface rather than resting on the substrate, they eliminate the need for constructing access roads, scaffolding, or other infrastructure that might disturb fragile habitats.
Floating dredges are equipped with adaptable components, such as suction nozzles and cutter heads, that can be adjusted to conform precisely to irregular or uneven bottom contours. This adaptability optimizes sediment removal efficiency while minimizing environmental impact by avoiding excessive disruption of aquatic ecosystems. The ability to carefully navigate around vegetation or wildlife areas makes floating dredges especially valuable for projects that require ecological sensitivity.
Several critical performance indicators often measure the operational efficiency of floating dredges. At this point, it is essential to emphasize that accurate measurement of metrics such as static head, discharge distance, and flow velocity is critical for optimizing dredging performance:
EDDY Pump’s floating dredges incorporate patented vortex impeller technology that excels at handling heavy solids and abrasive slurries. This technology reduces clogging risks and component wear, delivering dependable, high-performance operation even in the most demanding dredging applications.
Successful dredging projects begin with thorough planning and careful execution, accounting for site conditions, sediment characteristics, and environmental considerations. The selection of appropriate dredging equipment—whether floating dredges, small dredges, or specialized dredgers—depends on the unique requirements of each project. For instance, floating dredges are ideal for projects in shallow or hard-to-reach areas, while small dredges can be deployed for precision work in confined spaces. Cutter suction dredgers excel at breaking up compacted sediments, whereas hopper dredgers are better suited for deep-water applications.
Incorporating innovative design features, such as vortex impeller technology, can significantly enhance operational efficiency by reducing clogging and wear, enabling continuous, reliable sediment removal. Sustainable dredging practices are also a top priority, with a focus on minimizing sediment disturbance, using eco-friendly equipment, and maintaining high water quality standards. By carefully evaluating site conditions and selecting the right equipment, project managers can optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure that dredging operations are both effective and environmentally responsible.
The floating gold dredge has a rich history that traces back to the 19th century, when early gold prospectors sought more efficient methods to extract gold from riverbeds and placer deposits. Initially, these miners relied on rudimentary floating platforms equipped with manual bucket systems, in which steel buckets were attached in a continuous line to excavate and transport sediment, or on basic suction hoses for sediment removal from shallow waters. While effective for small-scale operations, these early designs were limited in capacity and often labor-intensive, requiring constant manual intervention to operate.
As mining technology progressed, the floating gold dredge underwent significant transformations. Innovations in pump mechanics, cutter heads, and flotation platforms gradually improved dredging capabilities. The introduction of centrifugal and slurry pumps enabled stronger suction and higher sediment throughput. Meanwhile, advancements in materials and engineering enhanced the durability and stability of dredges, enabling them to operate in more challenging environments.
Today, floating gold dredges are sophisticated machines that integrate hydraulic and electric systems designed for continuous, high-efficiency mining operations. These modern dredges combine mechanical strength with precision control systems, dramatically increasing gold recovery rates while reducing operational costs.
One of the key breakthroughs in modern floating gold dredges is the use of variable-frequency drives (VFDs) to regulate pump speed and suction power precisely. This technological advancement enables operators to fine-tune dredging parameters in real time, optimizing the separation of gold particles from the slurry and minimizing losses. The sluice box, with its adjustable slope and strategic placement, plays a crucial role in fine gold recovery by allowing heavier gold particles to settle to the bottom while lighter material is carried away. Water is used to wash away sand, gravel, and dirt, leaving the dense gold behind. Precise control over flow rates and pressure enables adaptation to varying sediment types and concentrations, thereby improving overall yield.
Additionally, contemporary dredges incorporate wear-resistant materials in critical components, such as impellers and seals. These materials withstand the abrasive nature of sediments typically found in gold mining environments, extending equipment lifespan and lowering maintenance frequency. Modular dredging tools further enhance operational flexibility, allowing miners to switch out or adjust components swiftly in response to changing site conditions, ensuring maximum efficiency.
A defining feature of EDDY Pump’s floating gold dredge systems is their clog-resistant design. Traditional dredge pumps often struggle to handle mixtures of sticky, coarse, or heavy sediments, leading to frequent clogging and costly downtime. In contrast, EDDY Pump’s patented vortex impeller technology promotes smooth passage of solids, significantly reducing clogging risks and maintaining consistent operation.
Moreover, EDDY Pump designs its dredges with quick-access service points, enabling field technicians to perform maintenance and repairs quickly without dismantling major assemblies. This focus on durability and serviceability minimizes project interruptions, keeping operations running efficiently.
For both artisanal miners seeking affordable, reliable equipment and industrial mining operations requiring high-capacity, durable dredges, EDDY Pump offers a proven solution that maximizes gold recovery while minimizing operational headaches.
The industrial dredge market benefits greatly from the versatility of floating dredges. Key applications include:
In a recent case, a Canadian mining company deployed an EDDY Pump industrial dredge floating system to clear sediment from a tailings basin, thereby increasing processing efficiency and reducing downtime compared to previous fixed-dredging methods.
Fixed dredges require significant infrastructure, including stable platforms and access roads, which limits their use on remote or sensitive sites. Conversely, floating dredges provide unmatched site access due to their mobility and reduced setup requirements. A small dredge is ideal for precision work or confined spaces where larger equipment cannot operate.
While fixed systems may deliver higher pumping power for large-scale, continuous operations, floating dredges offer flexibility, faster deployment, and lower environmental impact, making them preferable for many industrial dredging scenarios.
Selecting the right dredging tool is essential to maximizing the productivity of a floating dredge. Common options include:
Each dredging tool serves a specific purpose, and selecting the right one depends on the type of sediment and the project’s goals.
EDDY Pump’s floating dredge platforms feature modular connections, enabling rapid swapping of dredging tools. This feature enables operators to adjust their setup mid-project, optimizing performance across varying site conditions.
The modularity reduces downtime and increases operational flexibility, key benefits in dynamic dredging environments.
EDDY Pump supports a comprehensive range of dredging tools engineered for their floating dredge systems. This ecosystem includes heavy-duty cutter heads, adjustable suction nozzles, and specialized drag arms.
All attachments feature quick-connect interfaces for fast installation and maintenance, and are designed with wear-resistant materials to ensure longevity in even the most abrasive slurry applications.
Safety is a critical component of all dredging operations, given the involvement of heavy machinery, high-pressure pumps, and the handling of potentially hazardous materials. Operators must be thoroughly trained to manage equipment safely and respond effectively to emergencies, such as equipment malfunctions or unexpected sediment collapses. The use of personal protective equipment (PPE)—including hard hats, life jackets, and protective clothing—is mandatory to safeguard workers during dredging projects.
Regular maintenance of all equipment — from pumps and hoses to the main dredge body — is essential to prevent accidents and maintain operational efficiency. Ensuring that all machinery is properly equipped and functioning at optimal pressure levels reduces the risk of breakdowns. It enhances project safety. By prioritizing comprehensive safety protocols and ongoing operator training, dredging projects can minimize risks, protect personnel, and achieve successful outcomes.
One of the most significant advantages of deploying a floating dredge is that it eliminates the need to construct scaffolding or access roads. Traditional dredging often requires the construction of land-based infrastructure to transport and support heavy equipment, which can be expensive, time-consuming, and environmentally disruptive. Floating dredges operate directly on the water surface, enabling them to reach remote or environmentally sensitive locations without disturbing the terrain. This feature is especially valuable in wetlands, conservation areas, and shallow water bodies where ground disturbance must be minimized.
Floating dredges have a much smaller environmental footprint compared to conventional dredging equipment. Because they do not rely on heavy machinery moving across land, they greatly reduce soil compaction and vegetation damage. This preserves the natural habitat and reduces the risk of erosion. Additionally, the precision of floating dredging tools helps limit turbidity and sediment displacement, protecting aquatic ecosystems and water quality. The controlled sediment removal process aligns with environmental protection standards and promotes sustainable dredging practices.
Modern floating dredges often integrate with drone technology and remote control systems, elevating safety and operational efficiency. Drones provide aerial surveillance, site mapping, and real-time monitoring, enabling operators to gain enhanced situational awareness from a safe distance. Remote operation reduces the number of personnel required on-site, thereby lowering the risk of accidents in challenging or hazardous conditions. Furthermore, instant data from drones and control systems enable faster, more informed decision-making, improving dredging accuracy and project outcomes.
Implementing best practices in dredging projects is key to achieving efficient, sustainable, and safe operations. Minimizing sediment disturbance and using eco-friendly equipment helps protect aquatic ecosystems and maintain water quality. For smaller-scale projects, small dredges like the Piranha Mini Dredge offer a cost-effective, efficient solution, enabling targeted sediment removal with minimal environmental impact.
Leveraging advanced technologies, such as GPS navigation and automated control systems, can further improve operational efficiency and precision. Regular monitoring and maintenance of pumps, dredges, and related equipment ensures that operations remain efficient and downtime is minimized. Continuous training for operators is also vital, keeping teams up to date on the latest safety protocols and operational techniques. By adhering to these best practices, dredging operations can meet project goals while supporting long-term sustainability and the health of aquatic environments.
Purchasing a floating dredge is a significant capital investment (CapEx) suitable for companies with ongoing sediment removal needs. Ownership allows full control over equipment use and customization.
Alternatively, renting a floating dredge shifts costs to operational expenditure (OpEx), which is ideal for short-term projects or trial purposes. Rentals often include maintenance, support, and flexibility to upgrade to newer models.
EDDY Pump offers a comprehensive network of floating dredge units for rent, equipped with a range of dredging tools to meet diverse project requirements. Their rental programs provide rapid deployment, technical support, and flexible contract terms.
Clients gain access to premium equipment without upfront capital outlay, making rentals an attractive option for many businesses.
Whether buying or renting, EDDY Pump backs its floating dredge products with comprehensive warranties, performance guarantees, and responsive support services. These packages ensure reliable operation, provide support for maintenance and training, and help clients maximize the outcomes of their dredging projects.
The floating dredge is revolutionizing dredging projects by combining mobility, efficiency, and environmental responsibility. Its versatility across applications, from the floating gold dredge used in mining to the broader industrial dredge sector, underscores its critical role in modern sediment management.
With EDDY Pump’s clog resistant pumps, modular dredging tools and USA built platforms, our clients get solutions engineered for the toughest dredging environments.
A floating dredge is a dredging machine mounted on a pontoon or float-based platform, allowing it to operate directly on the water surface rather than from land. It’s most useful in lakes, rivers, shallow coastal areas, and other sites where traditional heavy equipment cannot easily be deployed. Floating dredges are ideal for remote or environmentally sensitive locations where access or ground disturbance must be minimized.
Key advantages include:
This depends on project frequency, duration, and budget. Purchasing makes sense for companies with ongoing dredging needs and frequent use. Renting is often better for short-term projects, trials, or when a lower upfront investment is preferred. Renting also reduces maintenance responsibilities and allows access to technical support from the supplier. However, for consistent or large-scale operations, ownership may offer better long-term value.
Floating dredges may not be ideal for very deep waters, sites with extreme waves or heavy currents, or areas where anchoring is difficult. They can also be less efficient for extremely large sediment volumes, which require higher pumping power.
Before selecting a floating dredge, check:
Operating a floating dredge safely and efficiently requires:
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.