





















EUR
en
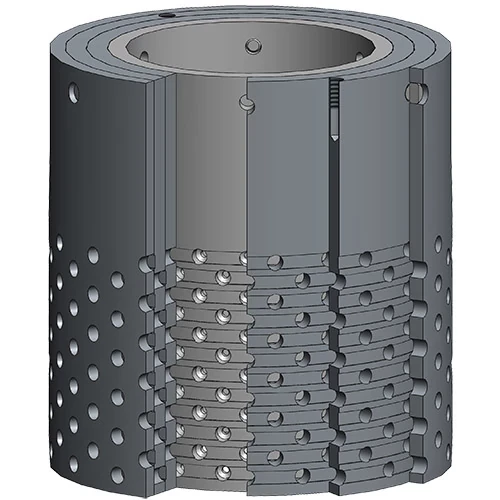
The cutter head is the front - line component of a cutter suction dredger, responsible for breaking up the seabed or riverbed material. It consists of a rotating drum with cutting teeth or blades attached. These teeth come in different shapes and sizes depending on the type of material to be dredged, such as soft silt, hard clay, or even rock.
Conduct a visual inspection of the cutter head before and after each dredging operation. Check for any signs of wear, damage, or missing teeth. Look for cracks in the drum or any deformation that could affect its rotation.
Use non - destructive testing methods like ultrasonic testing to detect internal defects in the cutter head structure, especially in areas prone to stress concentration.
Ensure proper lubrication of the bearings and gears within the cutter head assembly. Use high - quality lubricants suitable for marine environments and the specific operating conditions of the dredger. The lubrication schedule should be strictly followed, and the lubricant level should be regularly checked and topped up.
For the cutting teeth, if they are mounted on movable or adjustable mechanisms, lubricate the joints to ensure smooth movement and prevent seizing.
After each use, clean the cutter head to remove any accumulated sediment, debris, or abrasive particles. This can be done using high - pressure water jets. Pay special attention to the areas around the cutting teeth and the gaps between the teeth and the drum, as these are prone to clogging.
When cutting teeth are worn out or damaged, they need to be replaced promptly. First, identify the type and size of the teeth required for the specific cutter head model. Use proper tools to remove the old teeth, taking care not to damage the drum or the mounting structure.
Install the new teeth securely, ensuring they are properly aligned and tightened. Some teeth may require welding or bolting, and in such cases, follow the manufacturer's welding procedures or torque specifications for bolts.
If the cutter head drum has cracks or deformations, small cracks can be repaired using welding techniques. However, it is crucial to use the correct welding materials and procedures to ensure the structural integrity of the drum. For larger deformations or extensive damage, it may be necessary to replace the entire drum.
After repair or replacement, balance the cutter head to ensure smooth rotation. Imbalance can cause excessive vibration during operation, leading to further damage to the cutter head and other components of the dredger.
The suction pipe is responsible for transporting the slurry (a mixture of water and dredged material) from the cutter head to the pump. The ladder supports the suction pipe and allows it to be adjusted in height and angle to reach different dredging depths.
Regularly inspect the suction pipe for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Check the inner surface for abrasion caused by the slurry, especially in areas where the flow changes direction. The outer surface should be inspected for corrosion, which can be more severe in saltwater environments.
Use thickness gauges to measure the wall thickness of the suction pipe at regular intervals. If the thickness drops below the minimum acceptable level, it may be necessary to repair or replace the pipe section.
Lubricate the hinges, joints, and winch systems of the ladder regularly. These components are subject to frequent movement and can seize if not properly lubricated. Use lubricants that can withstand the harsh conditions of the dredging environment, including water, sediment, and varying temperatures.
Inspect the structural integrity of the ladder, looking for any signs of bending, cracking, or loose fasteners. The ladder should be able to support the weight of the suction pipe and withstand the forces exerted during dredging operations.
Small holes or cracks in the suction pipe can be repaired using patch welding. However, the welding process must be carefully controlled to avoid further damage to the pipe. For more extensive damage, such as large sections of corroded or abraded pipe, replacement of the affected section is necessary.
When replacing a section of the suction pipe, ensure proper alignment and welding (or other joining methods) to maintain the integrity of the pipe and the smooth flow of the slurry.
If the ladder has bent or cracked components, straightening or welding can be used for repair, depending on the severity of the damage. For loose fasteners, re - tighten or replace them as needed. In cases where the ladder structure is severely damaged, it may be more cost - effective to replace the entire ladder rather than attempting complex repairs.
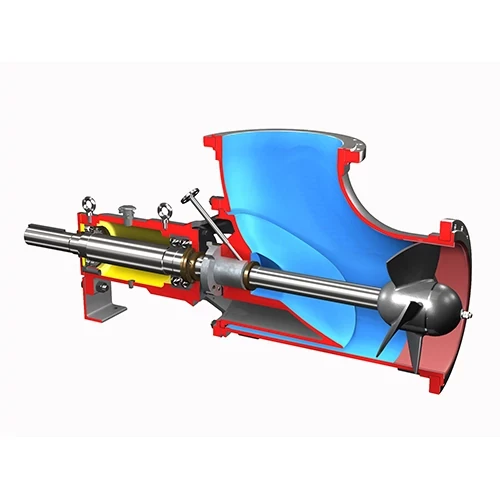
The suction pump is responsible for creating the vacuum that draws the slurry into the suction pipe and then pumping it to the discharge location. It typically consists of a centrifugal pump with impellers, casings, and seals.
Regularly inspect the impellers for wear, erosion, and damage. The impellers are in direct contact with the abrasive slurry, so they are prone to wear. Check for any signs of cavitation damage, which can occur due to improper flow conditions.
Inspect the pump casing for signs of wear, especially in the areas where the impeller rotates. Look for any cracks or deformations that could affect the pump's performance.
The seals in the suction pump, such as mechanical seals or packing seals, are crucial for preventing leakage. Regularly check the seals for wear and leakage. For mechanical seals, check the seal faces for any signs of damage or contamination. For packing seals, ensure the packing is properly adjusted and not worn out.
Lubricate the seals as per the manufacturer's recommendations. Some seals may require a constant supply of lubricating fluid, which should be monitored and maintained at the correct level.
Install vibration and temperature sensors on the suction pump to monitor its operating conditions. Excessive vibration can indicate problems such as impeller imbalance, misalignment, or bearing failure. Abnormal temperature rise can be a sign of overheating, which may be caused by insufficient lubrication, blockages, or worn - out components.
If the impellers are worn but still within repairable limits, they can be repaired using techniques such as hardfacing or coating. Hardfacing involves applying a wear - resistant material to the impeller surface to restore its thickness and functionality.
When impellers are severely damaged or worn beyond repair, they need to be replaced. Ensure that the new impellers are properly balanced and aligned with the pump shaft to avoid vibration issues.
Small cracks in the pump casing can be repaired using welding. However, the welding must be done carefully to avoid warping the casing or damaging internal components. For larger cracks or extensive damage, replacement of the casing may be necessary.
When seals are worn or leaking, they should be replaced immediately. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for seal replacement, as this process often requires precise alignment and handling of the seal components.
After seal replacement, conduct a pressure test to ensure there are no leaks and that the pump operates correctly.
Spuds are vertical poles that are used to anchor the cutter suction dredger during operation, providing stability. Winches are used to control the movement and positioning of the spuds, as well as other components like the ladder and suction pipe.
Regularly inspect the spuds for signs of bending, cracking, or corrosion. The spuds are subjected to high forces during dredging, so any structural damage can affect the stability of the dredger.
Check the spud shoes (if equipped) for wear. The spud shoes are in contact with the seabed and can be worn down over time, reducing their effectiveness in providing stability.
Inspect the winch drums for wear, especially the areas where the cables are wound. Check the cables for signs of fraying, corrosion, or excessive wear. Replace any damaged cables immediately.
Lubricate the winch gears, bearings, and other moving components regularly. The winches are subject to high loads and frequent use, so proper lubrication is essential for their smooth operation.
If the spuds have minor bends, they can be straightened using appropriate tools and techniques. However, care must be taken to avoid over - stressing the spud material. For cracked spuds, welding can be used for repair, but it is important to ensure the structural integrity of the spud after repair.
Worn - out spud shoes should be replaced with new ones that match the original design and specifications.
Damaged winch drums can be repaired using welding or other metal - working techniques, depending on the nature of the damage. However, if the damage is extensive, replacement of the winch drum may be necessary.
When replacing winch cables, use cables that meet the required strength and durability specifications. Properly spool the new cables onto the winch drums to ensure smooth operation.
The control system of a cutter suction dredger includes various sensors, controllers, and software that monitor and control the operation of the dredger. It is responsible for functions such as adjusting the cutter head speed, controlling the suction pump, and positioning the spuds and ladder.
Regularly calibrate the sensors used in the control system, such as depth sensors, pressure sensors, and flow sensors. Accurate sensor readings are essential for the proper operation and control of the dredger.
Check the sensors for any signs of damage or contamination. Clean the sensors as needed to ensure accurate readings.
Keep the controllers and software of the control system up - to - date. Manufacturers may release firmware or software updates that improve the performance, reliability, and functionality of the control system.
Back up the control system data regularly to prevent data loss in case of system failures.
When sensors fail or provide inaccurate readings, replace them with new sensors that are compatible with the control system. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for sensor installation and calibration.
If there are issues with the controllers or software, start by performing basic troubleshooting steps such as checking power supplies, connections, and error logs. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer's technical support or a qualified technician.
In some cases, it may be necessary to re - program or re - configure the controllers and software to resolve the issues. This should only be done by trained personnel to avoid further problems.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.