





















EUR
en
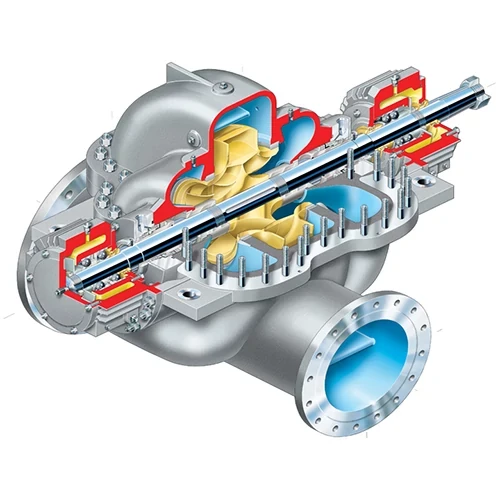
Centrifugal pumps are a type of hydraulic pumps that transform mechanical energy into kinetic energy of pressure to a fluid. Centrifugal pumps increase the velocity of fluids so that they can travel long distances.
Before checking the important points in a proper maintenance plan, the centrifugal pump’s environment, i.e. in which environment it is operating and how much it is exposed to, should be considered. This will help determine its performance, reliability, and efficiency.
To know the efficiency of the centrifugal pump that is already installed, mechanical, volumetric and hydraulic efficiency must be considered, the latter being the most essential factor in determining the overall efficiency. Among the activities for the correct maintenance of the centrifugal pump are the verification of gaskets and mechanical seals that will prevent leaks. In addition, it is significant to check the correct operation of the motor.
In ideal conditions, centrifugal pumps can operate indefinitely. Under adverse conditions, they often break down. For example, if the fluid being pumped is corrosive or contains abrasives, the pump will require more maintenance than is required under more favourable conditions. However, the life of any pump can be extended by proper maintenance procedures.
Most premature damage to a pump is caused by contamination, incorrect lubrication or alignment problems.
Contamination: A pump can become contaminated by debris from the fluid being pumped or when pump accessories are handled with dirty hands. A less obvious form of contamination occurs when air or other gases are trapped in the pump.
Incorrect lubrication:Like most machinery, centrifugal pumps need oil or grease to lubricate the bearings, but they also have additional lubrication requirements. Pump packings and seals are typically lubricated by the fluid flow. All these lubrication needs must be strictly met if maximum service life is to be achieved.
Misalignment: The strict alignment formula is often ignored. Misalignment of the pump and drive element causes vibration and excessive bearing wear. It also places unnecessary stress on the shaft. Pumps should be aligned according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
The following circumstances generally require a daily check:
Suction filter (when used): Check the difference in pressure between the pressure gauges on each side of the strainer. If the pressure drop increases, the filter requires cleaning.
Pump flow:Check suction and discharge pressure gauges to maintain pump performance.
Leakage at gaskets: There should be some leakage at the gaskets to keep them lubricated and to prevent outside air from entering the collar. The leakage should be at least twenty drops per minute.
External Seal and Injection Pressure: If the pump uses an external source to lubricate the seals or packings, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations to obtain the correct seal or injection pressure. Excessive hydraulic pressure can shorten the life of seals and gaskets.
Bearing temperature: Bearings that run too hot will wear prematurely and can cause damage to other accessories. On the other hand, liquid-cooled bearings should not be cooled too much, as condensation may occur and cause the bearings to rust. Check the temperature of the bearings with a pyrometer or thermometer. Many pump bearings normally run between 602C (1402F) and 6SQC (150 °F), which is too hot to touch.
Shaft rotation: (only during periods of Inactivity). Whenever the pump is shut down for an extended period, rotate the shaft manually one and a quarter turns to lubricate the bearings and prevent the shaft from binding.
Auxiliary piping: Leakage at connections.
Vibration of shaft and bearings:Use un medidor de vibración manual para medir la vibración de los cojinetes y del eje. La vibración no deberá exceder de 0.002″.
Power consumption: Make checking the power consumption of the pump a routine part of the operating routine. Excessive power consumption is a sign that the pump alignment, bearings, and other accessories need to be checked.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.