





















EUR
en
A froth slurry pump is a specialized type of centrifugal pump designed to handle frothy and aerated slurries typically encountered in mineral processing and flotation applications. Unlike conventional slurry pumps, froth slurry pumps are equipped with unique features such as a large impeller eye and extended shaft to prevent air entrainment and froth formation, allowing for efficient pumping of frothy mixtures. These pumps are essential in flotation processes where froth flotation is used to separate valuable minerals from gangue materials by selectively attaching air bubbles to mineral particles.
Froth slurry pumps are specifically designed to handle mixtures that contain a significant amount of gas or air, which is often present in flotation processes used in mining. These pumps can move the frothy slurry more efficiently compared to traditional pumps, which struggle with high froth volume factors.
The design of froth slurry pumps allows for the transportation of solids suspended in liquid without allowing them to settle. The high shear rates created by the impellers keep the solids well mixed with the liquid phase, ensuring consistent delivery.
The ability of froth slurry pumps to maintain a homogenous mixture reduces the risk of clogs in the pipelines. This characteristic is particularly important in systems with long transfer lines where solids could otherwise accumulate and cause blockages.
Froth slurry pumps are engineered to operate at lower power requirements compared to other types of pumps when dealing with frothy media. This efficiency is attributed to the optimized impeller design and the reduction of backpressure caused by air pockets.
The robust construction and careful design of froth slurry pumps contribute to a longer operational life. They are built to withstand the abrasive and corrosive nature of frothy slurries, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements.
Froth slurry pumps are versatile and can be used in various industries beyond mining, such as wastewater treatment, chemical processing, and pulp and paper manufacturing. Their ability to handle a wide range of viscosities and densities makes them adaptable to different processing requirements.
Froth slurry pumps handle frothy and aerated slurries by employing specialized features that prevent air entrainment and froth formation. These pumps are equipped with unique impeller designs and extended shafts that minimize the introduction of air into the pump chamber, allowing for efficient pumping of frothy mixtures without air locking or performance degradation. The large impeller eye and extended shafts create a barrier that separates air from the slurry, ensuring smooth flow and preventing froth buildup. Additionally, froth slurry pumps may incorporate features such as vortex breakers and adjustable suction liners to further enhance froth handling capabilities and maintain optimal pump performance in challenging operating environments.
The froth slurry pump prevents air entrainment and froth formation through specialized design features. Its large impeller eye and extended shaft are engineered to minimize the introduction of air into the pump chamber, reducing the likelihood of froth formation during operation. By maintaining a tight seal and effectively handling frothy slurries, the pump ensures efficient pumping without air locking or performance degradation. This design prevents froth formation and air entrainment, allowing for the smooth transportation of frothy mixtures in mineral processing and flotation applications.
These materials include frothy slurries containing air bubbles, aerated slurries, and mixtures of solids and liquids. Froth slurry pumps can handle various types of ores, minerals, and gangue materials typically found in flotation processes, such as sulfide ores, copper, zinc, lead, and precious metals. The pumps are also suitable for transporting abrasive particles, sediments, and tailings in mining operations. Froth slurry pumps exhibit versatility in handling complex mixtures of solids, liquids, and gases encountered in froth flotation and other industrial processes.
A froth slurry pump differs from a standard slurry pump in its specialized design to handle frothy and aerated slurries encountered in mineral processing and flotation applications. Unlike standard slurry pumps, froth slurry pumps feature unique features such as a large impeller eye and extended shaft to prevent air entrainment and froth formation. This design prevents air from being drawn into the pump, ensuring efficient pumping of frothy mixtures without air locking or performance degradation. Froth slurry pumps are equipped with specialized impeller designs and extended shafts that are tailored to handle the challenges posed by frothy slurries, making them essential for maintaining process efficiency and productivity in flotation processes.
Select a froth slurry pump specifically designed to handle frothy and aerated slurries encountered in flotation processes. Look for pumps with specialized impeller designs and extended shafts to prevent air entrainment and froth formation, ensuring efficient pumping of frothy mixtures.
Determine the required pump size and capacity based on factors such as the volume of froth-laden slurry to be handled, flow rate requirements, and process conditions. Choose a pump with sufficient capacity to meet the demands of the application without overloading the pump or compromising performance.
Consider the compatibility of pump materials with the abrasive and corrosive properties of the slurries being handled. Select pumps constructed from wear-resistant materials such as high-chrome alloys, rubber, or polyurethane to withstand the abrasive wear and erosion caused by frothy slurries.
Assess the efficiency and reliability of the pump, taking into account factors such as pump design, hydraulic performance, and maintenance requirements. Select a pump with a proven track record of reliability and efficiency to minimize downtime and maximize process productivity.
Froth slurry pumps handle high-density froths and viscous slurries by employing specialized design features and materials that are tailored to withstand the challenges posed by such conditions. These pumps typically feature large impeller eyes and extended shafts to prevent air entrainment and froth formation, allowing for efficient pumping of frothy mixtures without air locking or performance degradation. Froth slurry pumps are constructed from wear-resistant materials such as high-chrome alloys, rubber, or polyurethane, which can withstand the abrasive wear and erosion caused by high-density froths and viscous slurries. By incorporating these design elements, froth slurry pumps can effectively handle challenging operating conditions encountered in mineral processing and flotation applications, ensuring reliable and efficient performance.
The material of froth slurry pumps is crucial for withstanding the abrasive wear and erosion encountered in mineral processing and flotation applications. These pumps are commonly constructed from high-quality materials such as high-chrome alloys, rubber, or polyurethane. High-chrome alloys offer excellent abrasion resistance and are suitable for handling abrasive slurries containing solid particles. Rubber and polyurethane materials provide flexibility and resilience, making them ideal for applications where corrosion resistance and impact absorption are required. The choice of material depends on factors such as the properties of the pumped media, operating conditions, and specific application requirements.
In mineral extraction plants, froth slurry pumps are used to transport the frothy mixture produced during the flotation stage. This stage separates valuable minerals from the ore by attaching air bubbles to the particles, which then rise to the surface and form a froth.
Froth slurry pumps are utilized to transfer the underflow from thickeners in the mining industry. Thickeners are used to increase the solid concentration of slurries before they are sent to the next processing stage or storage.
Tailings, the material left over after the valuable minerals have been extracted, often contain fine particles and air bubbles. Froth slurry pumps are essential for managing the transport and disposal of tailings in an environmentally controlled manner.
In the papermaking process, froth slurry pumps are employed to move slurries containing fibers and chemicals. The air in the slurry helps to keep the fibers suspended and evenly distributed.
Froth slurry pumps are involved in circulating reagents and frothers used in flotation processes to enhance mineral recovery and separation. They ensure the efficient distribution of reagents throughout the flotation circuit, promoting optimal froth formation and mineral attachment to air bubbles.
In wastewater treatment facilities, froth slurry pumps can transport activated sludge, which often contains entrained air. The pumps must be capable of handling the varying consistencies and air contents found in wastewater applications.
Prior to reaching the froth slurry pump, the slurry is processed in a flotation cell. During this step, air bubbles attach to the valuable mineral particles, causing them to float and form a frothy mixture. This frothy slurry has a higher air content than typical slurries, necessitating a specialized pump that can handle the air-laden mixture without compromising performance.
Froth slurry pumps are engineered to manage the unique properties of frothy slurries. They often feature heavy-duty components and specialized impeller designs that create a vortex action to maintain the froth while preventing air entrapment and solids settlement. The selection of the pump is based on the specific characteristics of the slurry, including particle size, slurry density, and the required flow rate.
When the pump is activated, the motor drives the impeller, creating a low-pressure area that draws the frothy slurry into the pump. The impeller's rotation subjects the slurry to high shear forces, which help to keep the air mixed within the slurry and prevent sedimentation. Valves are strategically placed to control the flow and discharge pressure of the pump, ensuring that the system operates within the desired parameters.
To ensure continuous operation and prevent premature wear, froth slurry pumps require regular maintenance. This typically involves checking and replacing wear parts such as seals and bearings, inspecting the impeller for signs of wear, and cleaning the pump to remove any buildup of slurry residue. Proper maintenance helps to minimize downtime and extend the pump's lifespan.
The performance of froth slurry pumps is continuously monitored to detect any deviations from optimal operation. Key performance indicators include flow rate, discharge pressure, and vibration levels. If anomalies are detected, the pump may need to be taken offline for a detailed inspection. Common issues include misalignment, clogged impellers, and worn-out components, all of which can be addressed through targeted troubleshooting and corrective actions.
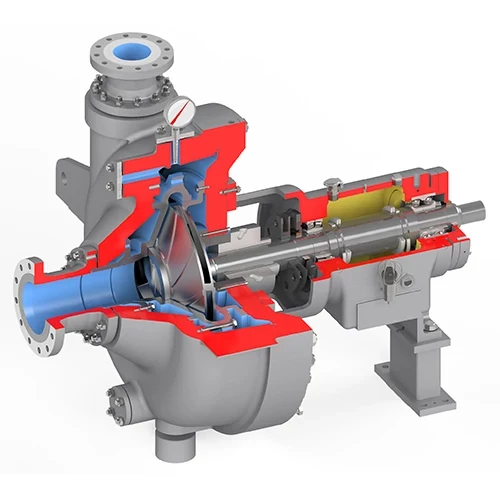
These components typically include an impeller, casing, shaft, bearings, and sealing systems. The impeller, with its unique design featuring a large eye and extended shaft, prevents air entrainment and froth formation, ensuring smooth pumping of frothy mixtures. The casing encloses the impeller and provides support, while the shaft transmits rotational energy from the motor to the impeller. Bearings support the shaft and impeller, allowing for smooth rotation. Sealing systems, such as gland seals or mechanical seals, prevent leakage and maintain pump efficiency.
Froth slurry pumps play a vital role in flotation processes in mining by efficiently handling frothy and aerated slurries encountered during mineral separation. These pumps facilitate the creation of stable froths and the transport of froth-laden slurries, which are essential for the selective recovery of valuable minerals from gangue materials. By effectively transferring frothy mixtures of air, water, and mineral particles within flotation cells and processing equipment, froth slurry pumps ensure optimal froth formation and mineral attachment to air bubbles. This promotes the separation of valuable minerals from undesired materials, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of flotation processes in mining operations.
Froth slurry pumps are designed to handle variable flow rates and operating conditions encountered in mineral processing and flotation applications. These pumps feature robust construction and specialized design features that allow them to adapt to changing process requirements and fluctuating operating conditions. The pumps are engineered to maintain efficient performance across a wide range of flow rates, ensuring consistent pumping of frothy slurries under varying process conditions. Froth slurry pumps are equipped with adjustable impeller settings and control mechanisms that enable operators to optimize pump performance and adapt to changes in operating parameters.
Froth slurry pumps play a pivotal role in mineral processing operations by facilitating the efficient handling of frothy and aerated slurries encountered in flotation processes. These pumps are essential for transferring froth-laden slurries containing minerals from various processing equipment, such as flotation cells and thickeners, to subsequent stages for further separation and refinement. By enabling the transportation of froth-laden slurries, froth slurry pumps contribute to the selective recovery of valuable minerals through flotation, enhancing process efficiency and productivity in mineral processing operations.
Conduct regular visual inspections of the froth slurry pump for any signs of wear, corrosion, or unusual damage. Check the impeller, casing, and all wetted parts for abnormalities.
Ensure that the impeller remains properly balanced to minimize vibration and stress on bearings and seals. Unbalanced impellers can lead to increased maintenance costs and reduced equipment life.
Inspect and replace seals and gaskets regularly to prevent leaks. Frothy slurries can be particularly hard on seals due to their abrasive nature, so choose seals made of materials that can withstand the slurry's composition.
Verify the alignment of the motor and pump periodically to avoid excess vibration. Misalignment can cause increased wear on bearings and reduce the efficiency of the pump.
Bearings should be checked frequently for excessive heat, noise, or play, which can indicate failure. Replace bearings according to the recommendations or before they fail completely.
For pumps with couplings, inspect them for looseness or wear. Couplings can become damaged from the pump's vibrations or misalignment, leading to operational issues. Regularly check the bolts and ensure they are tightened to the appropriate torque.
Froth slurry pumps often feature sealed bearing housings to protect the bearings from contamination by abrasive particles and water ingress. Sealed bearings help prevent premature bearing failure and reduce the risk of pump downtime due to bearing-related issues.
Froth slurry pumps may offer various shaft seal options such as gland packing, mechanical seals, or labyrinth seals to prevent leakage of abrasive slurries and hazardous fluids. Properly sealed shafts help maintain a safe working environment by preventing fluid leaks and minimizing the risk of environmental contamination or injury.
Some froth slurry pumps incorporate overload protection mechanisms such as overload sensors or thermal overload switches to prevent motor damage in case of pump overload or excessive operating temperatures. These features help safeguard pump components and prevent potential safety hazards associated with motor overheating or overloading.
Froth slurry pumps are typically constructed from robust materials such as high-chrome alloys, rubber, or polyurethane to withstand the abrasive wear and erosion encountered in mineral processing applications. Sturdy construction ensures pump reliability and minimizes the risk of pump failure or damage during operation.
Froth slurry pumps may be equipped with guarding and safety shields to protect personnel from rotating parts, pinch points, and other potential hazards. Safety shields help prevent accidental contact with moving components and enhance operator safety during pump maintenance and operation.
The working principle of a froth slurry pump involves efficiently handling frothy and aerated slurries encountered in mineral processing and flotation applications. These pumps feature specialized design elements, including a large impeller eye and extended shaft, to prevent air entrainment and froth formation during pumping. As the pump is activated, the impeller rotates, creating a vortex within the pump casing. This vortex generates suction at the inlet, drawing the froth-laden slurry into the pump. The specialized impeller design and extended shaft prevent air from being drawn into the pump, ensuring efficient pumping of frothy mixtures without air locking or performance degradation. The froth slurry is then transported through the pump and discharged through the outlet, facilitating the flotation process by transporting froth-laden slurries to subsequent processing stages for further separation and refinement.
There is foundry, machinery shop, assembly shop with strong production capacity. And the Pump test station test capacity reach to 13000m³/h. Our company skeleton staff has more than 20 years production management and import and export experience, scientific research personnel 32 people, employees 174 people.
A: A froth slurry pump is a type of positive displacement pump specifically designed to handle slurries containing gas or foam, commonly found in mining and mineral processing industries. It is used to transport viscous, abrasive, and corrosive materials that contain gas bubbles, ensuring continuous and efficient material transfer.
A: Froth slurry pumps are engineered to handle the unique challenges of pumping slurries with entrained air or gas. Unlike centrifugal pumps, which rely on velocity and pressure to move fluid, froth slurry pumps use a reciprocating or rotary motion to create a vacuum that draws the slurry into the pump and discharges it with minimal slip and separation of the gas from the solid particles.
A: Froth slurry pumps are widely used in mining operations for flotation circuits, tailings disposal, and ore concentration processes. They are also utilized in the chemical industry for handling slurries with suspended solids, in the paper industry for pulp transportation, and in wastewater treatment for conveying sewage sludge with high gas content.
A: When selecting a froth slurry pump, one must consider the characteristics of the slurry (such as density, viscosity, and abrasiveness), the required flow rate and pressure, the presence of gas or foam, the desired maintenance interval, and the compatibility of the pump materials with the slurry composition. Additionally, the physical layout of the plant and operational cost are important factors to consider.
A: Froth slurry pumps are usually constructed from high-grade cast iron, stainless steel, rubber-lined cast iron, or other corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the abrasive and corrosive nature of the slurries. Impellers and wear plates are often made from hardened alloys or composite materials to extend service life.
A: Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of froth slurry pumps. This includes routine inspections for wear and tear, cleaning of the pump and associated piping, lubrication of moving parts, monitoring of operational parameters (like temperature and pressure), and timely replacement of worn-out components like seals and bearings.
A: Froth slurry pumps are designed with robust construction and wear-resistant materials to handle abrasive materials. The impeller and other wetted parts are often reinforced or lined with hard materials like carbides or ceramics to reduce wear.
A: Slip refers to the difference between the actual flow rate of the slurry and the theoretical flow rate based on the pump's design. To minimize slip, it is important to select a pump with an impeller design that is suitable for the specific slurry characteristics and to operate the pump within its recommended range of flow rates and pressures.
A: Troubleshooting common issues with froth slurry pumps involves identifying the symptoms (like low flow rates, noisy operation, or leaks), checking the pump's alignment and mechanical integrity, inspecting the impeller and wear parts for damage, and verifying the proper functioning of control systems and safety devices.
A: A dump valve, located on the suction side of the pump, allows operators to drain the slurry from the pump and associated piping when shutting down the pump for maintenance. This prevents the slurry from solidifying or causing blockages, simplifying the maintenance process and reducing downtime.
A: Monitoring the operating conditions (like temperature, pressure, and flow rate) of froth slurry pumps ensures that the pump operates within its safe and efficient limits. This helps prevent overheating, wear, and premature failure of the pump and its components.
A: The presence of gas in the slurry necessitates the selection of a froth slurry pump that is specifically designed to handle gases without experiencing vapor lock or reduced efficiency. Pumps with a suitable suction capacity and an optimized impeller design are preferred for such applications.
A: Froth slurry pumps are generally suitable for continuous operation, provided they are correctly sized and maintained according to the manufacturer's recommendations. However, the duty cycle and operational demands must align with the pump's capabilities to avoid overheating and premature wear.
A: Froth slurry pumps play a critical role in maintaining the quality of the froth in mineral processing by ensuring consistent and efficient transportation of the slurry to the flotation cells. Proper pump selection and maintenance help in preserving the bubble size and distribution necessary for effective separation of minerals.
A: Multi-pump systems with froth slurry pumps offer several advantages, including redundancy for increased reliability, flexibility in managing varying flow requirements, and the ability to perform maintenance on one pump while the others continue to operate. Additionally, multi-pump systems can improve overall process efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
A: Proper start-up and shutdown protocols for froth slurry pumps involve gradually increasing or decreasing the flow and pressure to avoid hydraulic shocks and mechanical stress. These protocols help protect the pump from damage caused by sudden changes in operating conditions and ensure safe and reliable operation.
A: The impeller design of froth slurry pumps is critical for their performance. Impellers with a larger eye diameter, open vane design, and angled vanes can effectively handle frothy slurries with entrained air by reducing slip and preventing air lock formation.
A: Reverse flow conditions can cause damage to froth slurry pumps by creating hydraulic shocks and abrading the internal surfaces of the pump. To mitigate this risk, pumps are often equipped with check valves and operated with appropriate flow control measures.
A: The discharge pressure of a froth slurry pump must be sufficient to overcome system resistance and deliver the slurry to its destination. Higher pressures may be required for longer pipelines or when the slurry needs to be lifted to a higher elevation.
A: Froth slurry pumps are generally designed to cope with moderate variations in slurry density. However, significant changes in density can affect the pump's performance and efficiency.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.