




















EUR
en
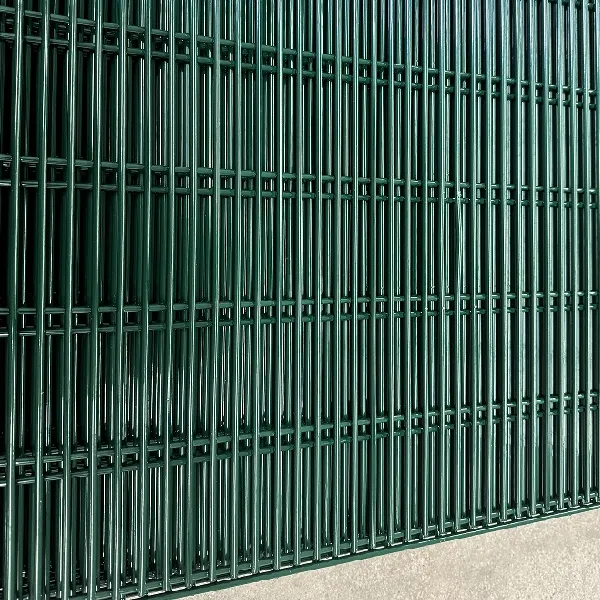
Wire mesh, also called welded wire fabric, is made of steel wires welded together in a grid pattern. It comes in rolls or sheets and is available in several forms:
Steel mesh: Standard welded wire mesh used in residential concrete applications.
Fiber mesh: Incorporates small synthetic fibers mixed directly into the concrete.
Stainless steel mesh: Offers corrosion resistance for damp or coastal environments.
Wire mesh reinforcement works well in situations where the concrete doesn’t need to support heavy loads. It’s most often used in:
Residential slabs and residential concrete driveways with light to medium traffic
Sidewalks and patios where expansion joints reduce stress
Garage floors or interior slabs with minor temperature changes
Projects over expansive soil, where minor movement or shrinkage could cause surface cracks
Pool decks where wire is easier to install and a more cost-effective option
Cost-effective for DIY projects and small pours
Helps prevent hairline cracks and maintains surface appearance
Easier and faster to install than rebar
Provides flexibility for irregular or curved slab shapes
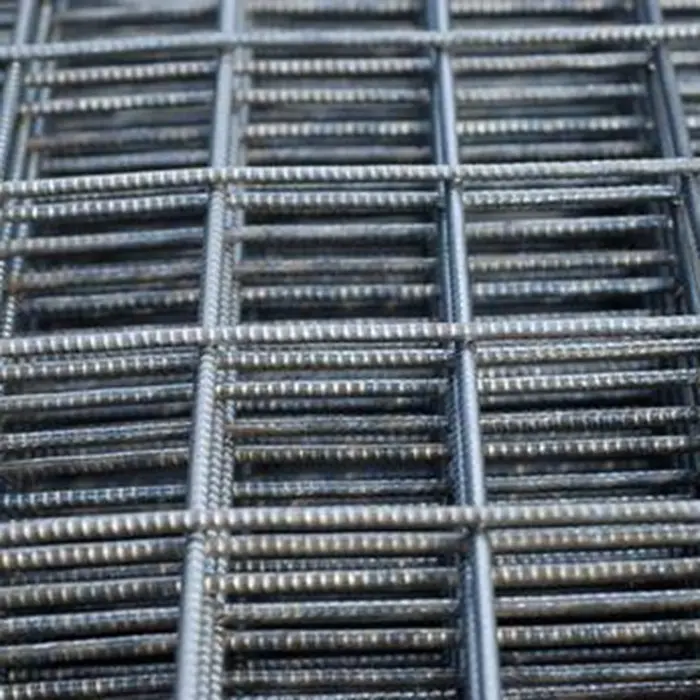
Rebar (short for reinforcing bar) consists of ribbed steel bars that create a solid framework inside the slab. These bars interlock with concrete, increasing its ability to handle tension and prevent large cracks.
Common types include:
Carbon steel rebar: Most widely used for general construction
Epoxy-coated rebar: Provides corrosion resistance for wet or salty conditions
Stainless steel or fiberglass rebar: Used in specialized environments
Rebar comes in different sizes and gauges, with higher grades offering greater tensile strength and load capacity.
Rebar is best for high-stress or load-bearing projects. Choose rebar when your concrete needs to handle heavy loads or expansive soil.
Common uses include:
Foundations and thick slabs supporting walls or heavy machinery
Commercial driveways and parking lots with frequent heavy traffic
Retaining walls, footers, and structural beams
Outdoor slabs exposed to freezing, thawing, or large temperature changes
Provides superior load-bearing capacity
Reduces risk of large structural cracks
Maintains slab integrity in high-traffic or industrial environments
Ideal for heavy-duty construction and thick concrete slabs
Rebar has higher tensile strength, allowing it to withstand bending and heavy loads without cracking. It’s ideal for thick slabs or foundations where the structure must bear significant weight.
Wire mesh provides basic reinforcement that holds the slab together if small cracks form. It’s best for lighter applications and projects focused on preventing surface defects.
Rebar typically comes with a higher upfront cost and requires more time to install, but it delivers superior strength and long-term reliability for demanding environments. It’s the better option for commercial projects, large slabs, or areas exposed to heavy traffic.
Wire mesh is more affordable and easier to install, making it popular for residential or DIY projects. It’s lightweight, flexible, and can be rolled out quickly, which saves time on smaller pours while still providing adequate crack resistance.
Using wire mesh where heavy loads are expected can lead to cracking or slab failure. Always consider the traffic type, soil condition, and slab thickness before deciding.
Both wire mesh and rebar must be embedded properly in wet concrete, not resting directly on the ground.
Place wire mesh near the slab’s middle to prevent surface cracks.
Position rebar grids about one-third from the bottom of the slab for optimal load distribution.
Wire mesh may seem like a cost saver, but it’s not suited for commercial projects with frequent heavy loads. Conversely, rebar may be excessive for light-use patios or sidewalks.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.