




















EUR
en
River sand is a naturally occurring granular material composed of finely divided rock and mineral particles. It is typically found in river beds and river banks due to erosion and sedimentation processes carried out by flowing water over thousands of years. M Sand, also known as Manufactured Sand, is a type of sand produced by crushing rocks, quarry stones or larger aggregates into sand-sized particles. It is an alternative to river sand and is manufactured through a process that involves crushing, screening, and washing to ensure that it is free of impurities.
River sand, due to its properties and availability, has several uses in various industries and applications. Here are some common uses of river sand: Construction: River sand is widely used in the construction industry for various purposes, such as: Mixing with cement to make concrete. Mixing with lime to make mortar. Mixing with other materials for plastering walls. Bedding material for laying pipes and utility lines. Landscaping: River sand is used in landscaping projects for: Creating beach-like settings in gardens or around water features. Mixing with soil to improve drainage in gardens or plant beds. Sports Fields: River sand is used in sports field construction for: Creating well-draining surfaces for playing fields like baseball diamonds, volleyball courts, and horse arenas. Sandblasting: River sand is used in sandblasting operations to: Clean and prepare surfaces by propelling sand at high speeds to remove paint, rust, or other coatings. Filtering Water: River sand can be used in water filtration systems to: Remove impurities and particles from water in applications like swimming pool filters or wastewater treatment plants. Manufacturing: River sand is used in the manufacturing industry for: Making glass. Producing ceramics. Creating molds for metal casting. Aquariums and Fish Tanks: River sand can be used as substrate in aquariums and fish tanks to: Create a natural look for aquatic environments. Provide a habitat for beneficial bacteria.
Manufactured Sand (M Sand) is a versatile material that finds applications in various industries and construction activities. Here are some common uses of M Sand: Concrete Production: M Sand is preferred in concrete production due to its consistent particle size distribution, which can enhance the strength and durability of concrete structures. Brickwork: M Sand is used in brickwork as a replacement for river sand in the mortar mix for better bond strength and durability. Plastering: M Sand is commonly used for plastering walls and ceilings, providing a smooth finish and improving workability. Manufactured Sand Blocks: M Sand is used to make concrete blocks, which are widely utilized in construction for building walls, partitions, and other structural elements. Asphalt Production: M Sand is sometimes used in the production of asphalt mixtures for road construction to improve the workability and quality of the mix. Tile Manufacturing: M Sand is used in tile manufacturing processes to enhance the strength and durability of tiles.
The debate over whether river sand is better than manufactured sand (M Sand) often depends on the specific application and regional considerations. Here are some points where river sand may be considered better than manufactured sand: Advantages of River Sand: Natural Properties: River sand is a naturally occurring material with rounded grains that provide better workability and bonding in concrete and mortar compared to the angular grains of manufactured sand. Proven Performance: River sand has been traditionally used in construction for centuries and has a track record of successful performance in various applications. Availability: In some regions, river sand may be more readily available and cost-effective compared to manufactured sand due to local geological factors. Silt Content: River sand generally has lower silt content compared to manufactured sand, which can be beneficial in certain applications. Sustainability: Using river sand in construction can sometimes be considered more sustainable, especially in areas where excessive mining of river sand is regulated to protect ecosystems. Disadvantages of Manufactured Sand (M Sand): Quality Concerns: The quality of manufactured sand can vary depending on the source material and the production process, potentially leading to inconsistencies in particle size distribution and impurities. Shape and Texture: The angular and rough texture of manufactured sand may require more water and cement to achieve the desired workability and strength in concrete compared to river sand. Environmental Impact: The production of manufactured sand involves crushing rocks or quarry stones, which can have environmental implications such as energy consumption and emissions. Regulatory Restrictions: In some regions, regulations may limit the use of manufactured sand in certain applications due to concerns about quality standards and long-term performance.
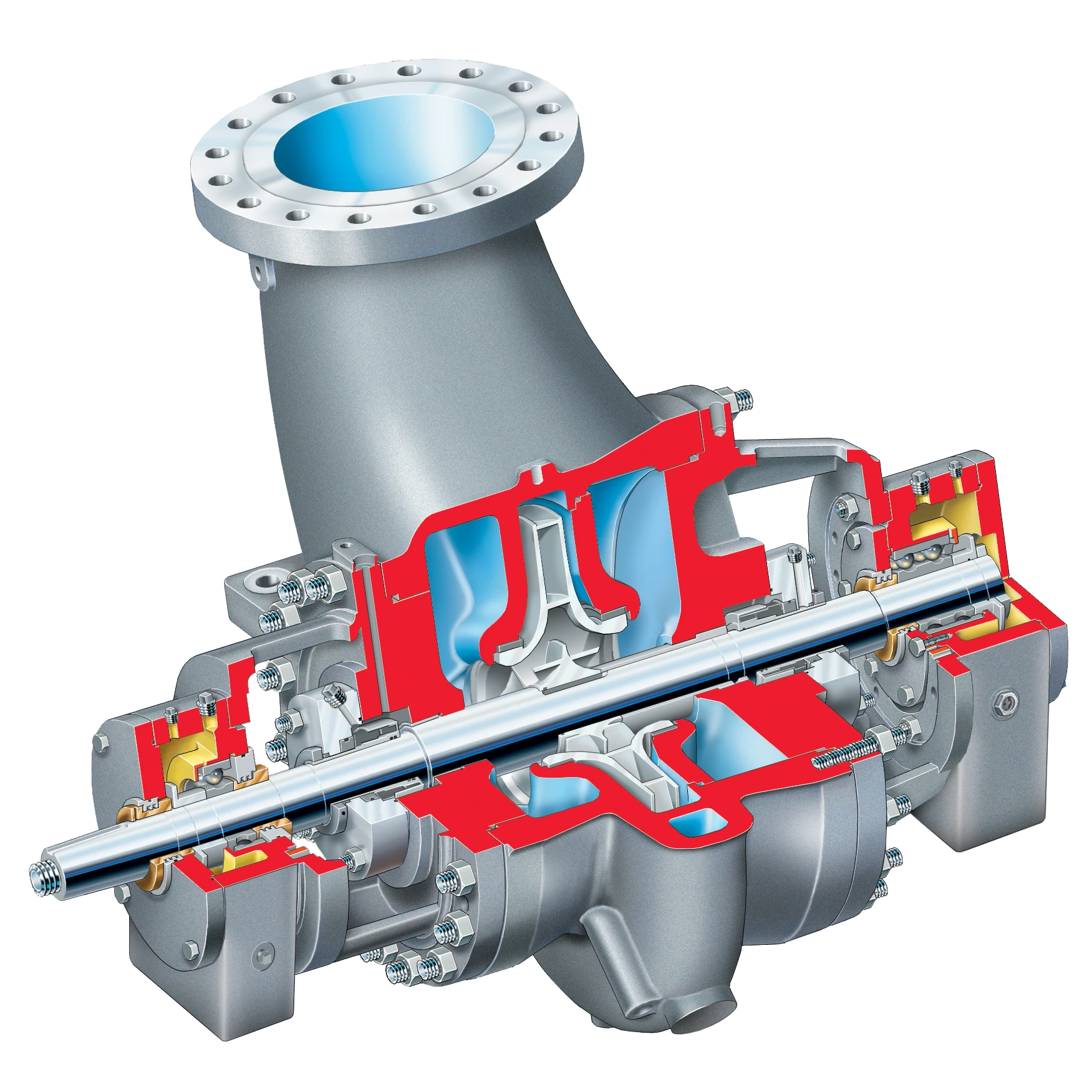
Pumping river sand for various applications, such as construction or dredging, typically involves the use of specialized equipment known as dredging pumps. Here are the general steps involved in pumping river sand: Dredging Pump: A high-capacity pump designed for handling large volumes of sand and solids. Suction Hose: A flexible hose connected to the pump used to draw in the sand-water mixture. Discharge Hose: Another flexible hose used to transport the pumped sand to the desired location. Dredger or Barge: A vessel equipped with the necessary machinery for pumping and transporting sand.
Positioning the Equipment: The dredger or barge is positioned near the area where sand extraction is required, such as a riverbed, lake, or seabed. Lowering the Suction Pipe: The suction pipe or hose is lowered into the water or sediment to the desired depth where sand needs to be pumped from. Creating Suction: The pump is activated, creating a vacuum that draws in a mixture of sand and water through the suction pipe. Transporting the Mixture: The pump forces the sand-water mixture through the discharge pipe/hose, moving it to the designated location, such as a processing plant, construction site, or containment area. Separation of Sand and Water: In some cases, the pumped mixture may be processed to separate the sand from the water before the sand is used for its intended purpose. Continuous Operation: Sand pumping is typically a continuous operation where the pump runs consistently to extract and transport sand efficiently. Monitoring and Adjustments: Operators monitor the pumping process, adjusting pump speed and flow rates as needed to maintain optimal performance and prevent clogging or damage to the equipment.
Bookmark
Daniel Féau processes personal data in order to optimise communication with our sales leads, our future clients and our established clients.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.